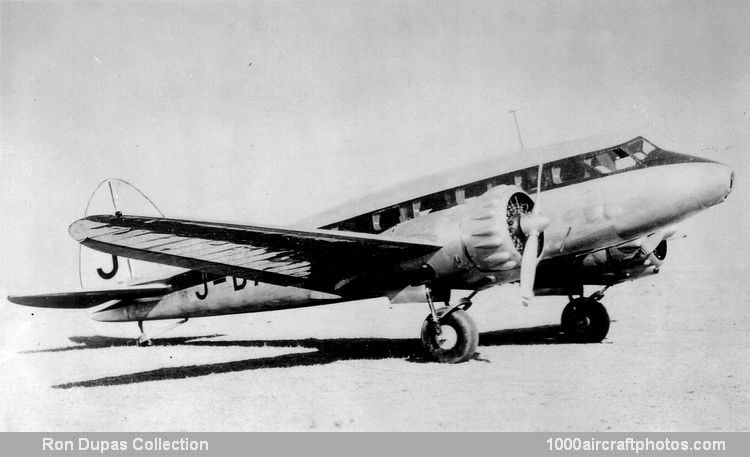
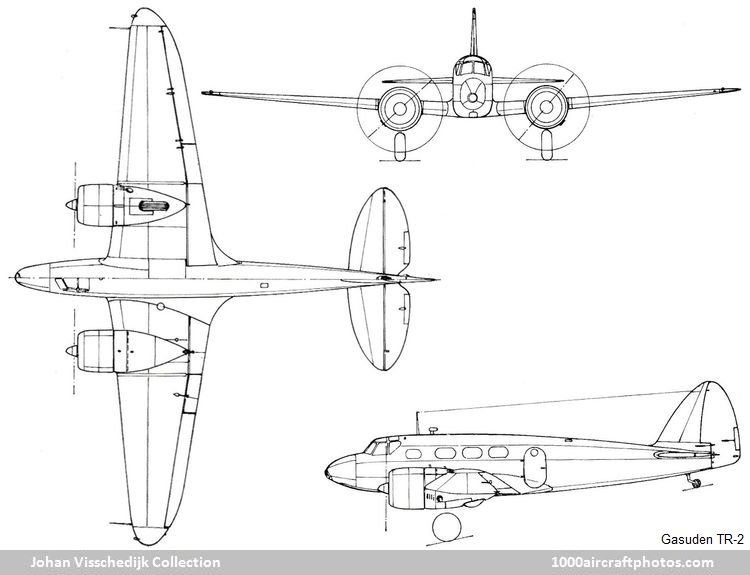
Design features were quite advanced for that period in Japanese aircraft development. Specifications for the new design were:
- Similar power and payload to that of the Airspeed Envoy, more than 186 mph (300 kmh) maximum speed, and
--------932 mls (1,500 kmh) range.
- Two 240 hp Gasuden Jimpu 5A nine-cylinder air-cooled radial engines, driving Sumitomo two-bladed fixed-pitch
--------metal propellers.
- All-metal construction with fabric covered control surfaces.
- Wing flaps of large area and simple operating mechanism. Ailerons were also to operate as flaps.
- Manually operated retractable landing gear to ensure reliability.
- Pneumatically operated flaps, wheel brakes and fuel dump valve.
- Narrow elliptical fuselage cross-section to reduce drag, hence the two pilots were seated in tandem with dual
--------control. Navigation and radio equipment were to be located in the rear co-pilot's position.
- Passenger seats were staggered to allow maximum seat width in the narrow fuselage. Standard seating was four,
--------increasable to six.
- Large windows to provide good cabin lighting and visibility for passengers. Lavatory located in the rear of the cabin.
- Cargo stowage in the nose (66 lb, 30 kg), under the wing center section of the fuselage and in the rear fuselage
--------(132 lb, 60kg each).
- Conversion capability to be offered for aerial survey/ observation, ambulance and crew training.
While being flight tested by Hideo Muramatsu on June 22, 1938, the port landing gear failed to lower. After burning off fuel for about two hours, an emergency landing was made with the port landing gear still retracted. After repairs to the damaged structure, the aircraft was shipped from Kobe to Taiwan. While en route an accident on board the ship caused further damage and the aircraft was returned to the Gasuden Factory where it lingered indefinitely.