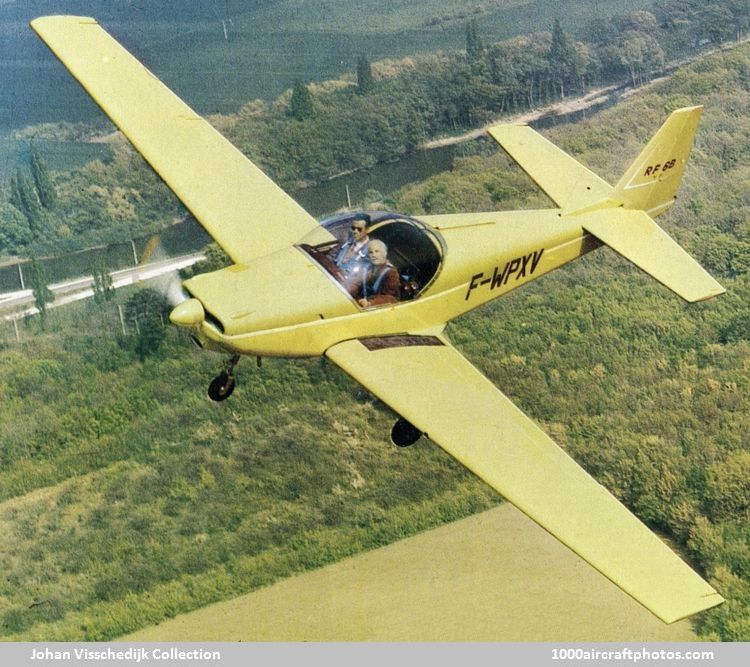
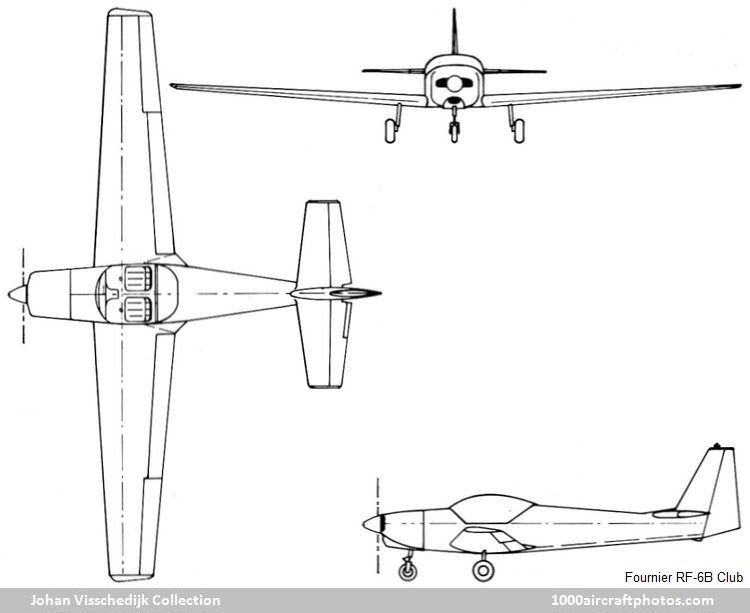
While the prototype was powered by a 90 hp Rolls-Royce Continental O-200-E four-cylinder horizontally-opposed air-cooled engine, driving a Hoffmann two-blade metal fixed-pitch propeller with spinner, the production aircraft was powered by a more powerful engine and had a longer nose.
Fournier had adopted a production concept that incorporated a considerable degree of sub-contract manufacture, this was unviable and the company collapsed. However, René Fournier formed Fournier Aviation in 1978, bringing together the assets of Avions Fournier and the Fournier Design Office, and continued the RF-6B-100 production.
The last aircraft on the production line, c/n 44, was fitted with a more powerful 120 hp Avco Lycoming O-235-L2A four-cylinder horizontally-opposed piston engine. Designated RF-6B-200 and registered F-GANF, this aircraft was first flown on August 16, 1980, and received DCAG certification on November 7, 1980. This type was subsequently built under license in the UK as as the Slingsby T67 Firefly.
In all, 45 aircraft were built: 1 RF-6B (c/n 01), 43 RF-6B-100 (c/n 1 to 43), 1 RF-6B-200 (c/n 44). Below the RF-6B-100 specifications.
Type: Two-seat aerobatic, training and sporting aircraft.
Wings: Cantilever low-wing monoplane. Wing section NACA 23015 at root, NACA 23013 at tip. All-wood single-spar structure with plywood and Dacron covering. Frise-type ailerons of wooden construction, Dacron covered. Plain trailing edge flaps of wooden construction with Dacron covering.
Fuselage: All-wood oval structure, plywood covered.
Tail unit: Cantilever structure of wood with Dacron covering. Fixed-incidence tail plane. Trim tab in port elevator.
Landing gear: Non-retractable tricycle type. Oleo-pneumatic shock-absorbers on all units. Steerable nose wheel. Main-wheel tires size 380 x 150. Nose wheel tire size 300 x 100. Hydraulic disc brakes.
Power plant: One 100 hp Rolls-Royce Continental O-200-A four-cylinder horizontally-opposed air-cooled engine, driving a Hoffmann two-blade wooden fixed-pitch propeller with spinner. Fuselage fuel tank, immediately aft of firewall. Refueling point on fuselage upper surface, forward of windscreen.
Accommodation: Two seats side-by-side under transparent canopy, which swings upward and aft for access to cockpit. Dual controls standard. Cockpit heated and ventilated. Baggage space aft of seats.
Systems: Hydraulic system for brakes only. Electrical power supplied by 12V engine-driven alternator.
Electronics and equipment: Navigation and communication radios optional. Blind-flying instrumentation optional.
Span: 34 ft 5.5 in (10.50 m)
Length: 22 ft 11.75 in (7.00 m)
Height: 8 ft 3 in (2.52 m)
Wing area: 139.9 sq.ft (13.00 sq.m)
Wing chord, at root: 5 ft 0.25 in (1.53 m)
Wing chord, at tip: 2 ft 8.75 in (0.83 m)
Wing incidence: 3°
Wing aspect ratio: 8.5
Wing dihedral: 3° 30'
Ailerons area (total) : 11.52 sq ft (1.07 sq.m)
Trailing edge flaps area (total): 16.36 sq ft (1.52 sq.m)
Rudder area: 7.97 sq ft (0.74 sq.m)
Tail plane span: 11 ft l.75 in (3.40 m)
Tail plane area: 17.76 sq ft (1.65 sq.m)
Elevators area, incl. tabs: 10.76 sq ft (1.00 sq.m)
Propeller diameter: 5 ft 9 in (1.75 m)
Propeller ground clearance: 11 in (0.28 m)
Empty weight: 1,102 lb (500 kg)
Max take off weight, aerobatic: 1,587 lb (720 kg)
Max take off weight, utility: 1,653 lb (750 kg)
Wing loading: 11.8 lb/sq ft (57.7 kg/sq.m)
g limits: + 9/- 4.5
Power loading: 16.53 lb/hp (10.07 kg/hp)
Fuel capacity: 21.13 gal (80 l)
Oil capacity: 1.06 gal (4 l)
Never exceed speed: 186 mph (300 kmh)
Max level speed: 124 mph (200 kmh)
Cruise speed: 112 mph (180 kmh)
Stall speed: 53 mph (85 kmh)
Min sinking rate, engine off: 6.6 ft (2.0 m)/sec
Max climb: 690 ft (210 m)/min
Take off to 50 ft (15 m): 950 ft (290 m)
Landing from 50 ft (15 m): 820 ft (250 m)
Landing run, no braking: 655 ft (200 m)
Service ceiling: 13,125 ft (4,000 m)
Range: 404 mls (650 km)